CNC vs. 3d Printing: What Are the Differences?
Navigation
- What Is CNC Machining?
- What Is 3D Printing?
- What Are the Differences Between CNC and 3D Printing?
- What Are the Limitations of CNC vs. 3D Printer?
- Will 3D Printing Replace CNC?
- Can 3D Printing and CNC Machining Be Used Together in a Manufacturing Process?
- Final Words
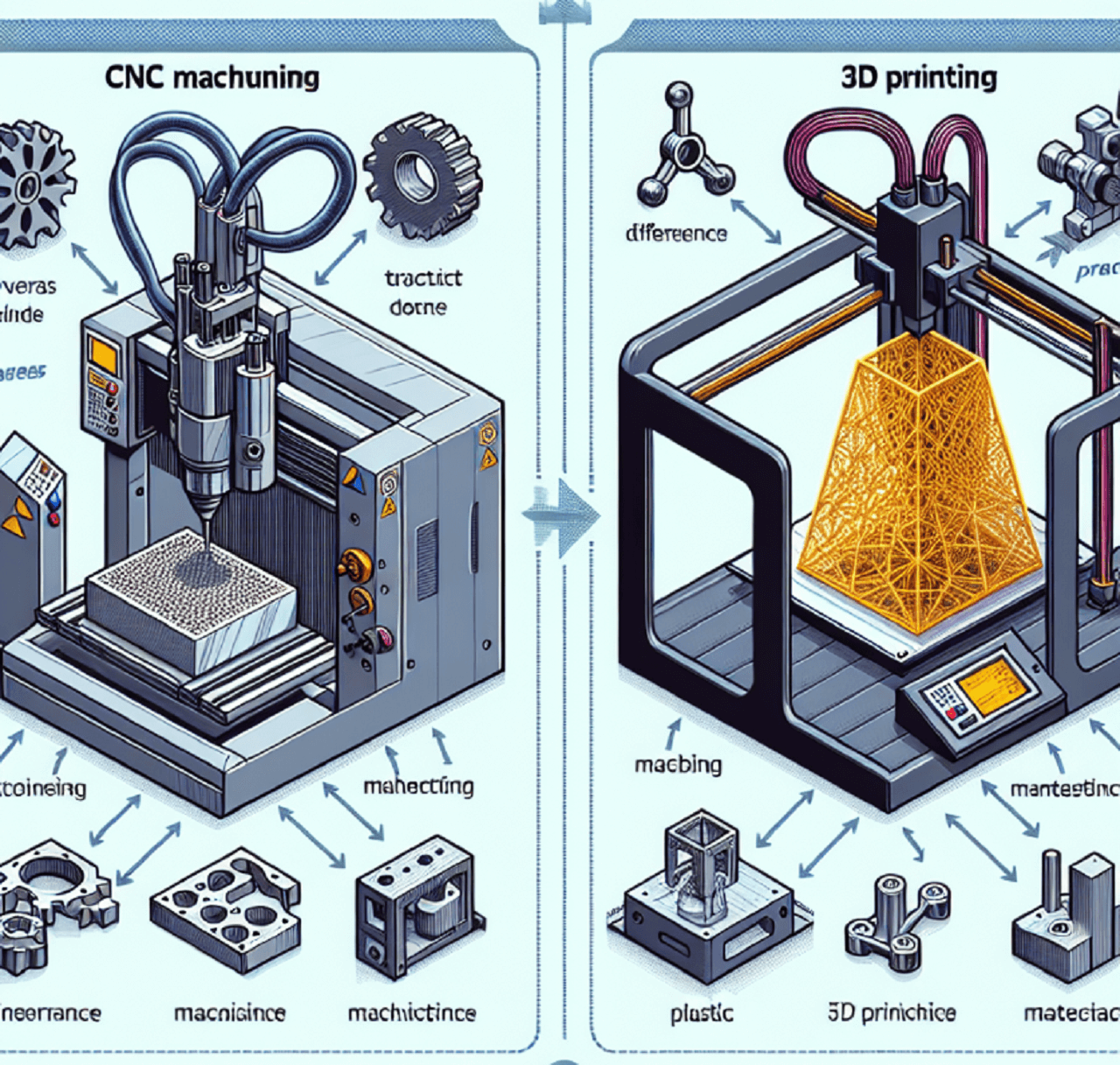
In the manufacturing area, CNC machining and 3D printing are two pivotal technologies, each with unique strengths and applications. This article aims to dissect the differences between CNC machining and 3D printing, focusing on aspects such as the manufacturing process, material use, precision, and environmental impact, among others.
What Is CNC Machining?
CNC (Computer Numerical Control) machining is a subtractive manufacturing process that utilizes computerized controls and machine tools to remove layers from a solid block of material, shaping the final product. This technology excels in producing high-precision parts with excellent surface finishes, finding its place in industries requiring utmost accuracy, such as aerospace, automotive, and healthcare.
What Is 3D Printing?
Contrary to CNC’s subtractive nature, 3D printing is an additive manufacturing technique that creates objects layer by layer. This process begins with a digital model from which the printer constructs the item by successively adding material, making it an ideal choice for prototyping, complex designs, and customized products. The versatility of 3D printing materials, including plastics, resins, and metal powders, opens up a broad spectrum of applications across various sectors.The choices in 3D printing methods, such as SLS and FDM, are pivotal in that they cater to a broad spectrum of applications across various sectors, each offering unique benefits and considerations that can influence the outcome of a project.
What Are the Differences Between CNC and 3D Printing?
| Feature | CNC Machining | 3D Printing |
|---|---|---|
| Manufacturing Process | Subtractive: Carves out from a block | Additive: Builds up layer by layer |
| Material Use | Wide variety: Metals, plastics, wood | Mainly plastics, resins, metal powders; expanding but still narrower |
| Precision and Surface Quality | High precision; smooth finish often without need for post-processing | High precision with potential need for post-processing to smooth out |
| Complexity and Design Freedom | Can be limited by tool access and process in creating complex geometries | Excels in creating complex structures and internal features CNC cannot |
| Production Speed and Cost | More economical for large-volume production due to rapid material removal | Faster and cost-effective for small runs or customized items |
| Environmental Impact | Generates waste material from subtractive process | Minimal waste, more sustainable by adding material only where needed |
| Application Scope | Ideal for industries needing durable, high-precision parts | Suits rapid prototyping, complex structures, and customization |
CNC vs. 3d Printing: Manufacturing Process
- CNC Machining embodies a subtractive process, meticulously carving out the desired shape from a solid block of material. This method is akin to sculpting, where the artist reveals the form within the marble by removing what is not needed. It’s a process of reduction, focusing on precision and adherence to the original design specifications.
- 3D Printing, in contrast, is inherently additive, constructing objects layer by successive layer from the bottom up. This approach allows for the conservation of materials and affords the ability to craft intricate details and complex geometries that would be difficult, if not impossible, to achieve through traditional subtractive methods. It’s akin to building with blocks, where each piece added contributes to the whole without waste.
CNC vs. 3d Printing: Material Use
- CNC Machining showcases its versatility by accommodating a wide variety of materials, including but not limited to metals, plastics, and wood. This broad material compatibility ensures its applicability across a diverse range of industries, from aerospace components crafted from high-strength alloys to custom wooden furniture pieces.
- 3D Printing, while initially more limited in its material range to primarily plastics and resins, has seen an expansion into metal powders and beyond. 3D Printing has advanced in its material capabilities, with technologies like SLS and SLA further widening the versatility of 3D printing materials. Understanding the nuances when choosing between these polymer 3D printing technologies is essential for optimizing product development.Despite this growth, the spectrum of materials suitable for 3D printing, though impressive, does not yet match the extensive array accessible to CNC machining.
CNC vs. 3d Printing: Precision and Surface Quality
- CNC Machining sets the standard for precision and surface finish, producing parts that meet exacting tolerances with surfaces so smooth they often require no further finishing. This level of accuracy is critical in applications where the fit and function of components are paramount.
- 3D Printing, while capable of achieving high levels of precision, typically leaves a texture that may necessitate post-processing to smooth out. Although these additional steps can achieve a comparable finish, they introduce extra time and effort into the production process.
CNC vs. 3d Printing: Complexity and Design Freedom
- 3D Printing excels in its ability to create designs of remarkable complexity with ease, including features such as undercuts, internal channels, and intricate lattices that would challenge conventional CNC machining. This capability unleashes unparalleled design freedom, enabling the realization of shapes and structures that push the boundaries of traditional manufacturing.
- CNC Machining, despite its adaptability and strength in producing a wide range of shapes and sizes, faces limitations when it comes to extremely complex geometries, particularly those involving internal structures. While capable of producing many intricate designs, the constraints of tool access and the nature of the subtractive process can limit its scope.
CNC vs. 3d Printing: Production Speed and Cost
- For limited runs or custom pieces, 3D Printing offers a swift and cost-efficient route from design to finished product, bypassing the need for complex setup or tooling. This makes it an ideal choice for prototypes or items tailored to specific needs.
- CNC Machining is more advantageous for larger-scale production. Its capacity for rapid material removal and the ability to quickly produce multiple parts from a single block make it economically viable, especially as production numbers increase.
CNC vs. 3d Printing: Environmental Impact
- The subtractive nature of CNC Machining inherently results in material waste, as excess material is removed and often not reused, presenting a greater environmental footprint.
- 3D Printing advocates for a greener approach to manufacturing. By adding material only where needed and minimizing excess, it stands as a more sustainable option, aligning with modern ecological concerns.
CNC vs. 3d Printing: Application Scope
- CNC Machining has established itself as a cornerstone in industries that demand the utmost in durability and precision. Its role in producing critical components for automotive, aerospace, and mechanical applications underscores its importance in high-stakes environments.
- 3D Printing has carved out its niche in prototype development, complex component production, and the medical field. Its ability to rapidly turn ideas into tangible items and customize solutions on the fly has revolutionized design and manufacturing processes, making it an invaluable tool for innovation and customization.
What Are the Limitations of CNC vs. 3D Printer?
CNC machining, while precise, can be resource-intensive, requiring significant material and energy, especially for complex parts. Its capabilities are also somewhat constrained by the geometry of the parts it can produce. On the other hand, 3D printing, although versatile in design, sometimes falls short in material strength and durability, limiting its use in applications requiring high-performance materials.
Will 3D Printing Replace CNC?
While 3D printing offers remarkable advantages in terms of design flexibility and waste reduction, it is unlikely to replace CNC machining entirely. Each technology serves distinct purposes, with CNC being indispensable for the high-volume production of metal parts and items requiring exceptional precision and durability. The future likely holds a complementary relationship between these technologies, leveraging the strengths of each to meet the diverse needs of modern manufacturing.
Can 3D Printing and CNC Machining Be Used Together in a Manufacturing Process?
A: Yes, combining 3D printing and CNC machining in a single manufacturing process can leverage the strengths of both technologies. This hybrid approach allows for the creation of complex, custom designs with the additive process of 3D printing, followed by CNC machining to achieve precise tolerances and superior surface finishes. This method is particularly beneficial in industries such as aerospace and medicine, where complex geometries and high precision are required.
Final Words
Selecting between CNC machining and 3D printing is a nuanced decision that requires careful analysis of project demands. While CNC offers unmatched precision for large-scale productions, 3D printing stands out for its innovative design capabilities and rapid prototyping. In this landscape of manufacturing technologies, Shenzhen Qisiyin 3D Printing Technology (QSYrapid) emerges as a beacon of additive manufacturing excellence.
With over 30 years of dedicated service, QSYrapid’s offerings encompass more than robust prototyping and 3D printing services. In a landscape where lead times can make or break a product’s success, QSYrapid’s instant 3D printing solutions stand out as a transformative asset, offering on-demand production capabilities that keep pace with the fast-moving demands of modern manufacturing.Their expansive array of over 100 precise 3D printers, coupled with a proprietary instant quoting system, establishes QSYrapid as a critical player in the transition toward efficient, tailored manufacturing solutions. As we look toward a future where precision, speed, and sustainability are paramount, QSYrapid continues to deliver on all fronts-ushering in an era where design potential is boundless, underpinning the ever-evolving synergy of CNC machining and 3D printing techniques.