Resin 3D Printing vs. Filament 3D Printing—Essentials You Should Know
Navigation
- What Is Resin 3D Printing?
- Advantages of Resin 3D Printing
- Disadvantages of Resin 3D Printing
- What Is Filament 3D Printing?
- Advantages of Filament 3D Printing
- Disadvantages of Filament 3D Printing
- Resin 3D Printing vs. Filament 3D Printing: Accuracy and Resolutions
- Resin 3D Printing vs. Filament 3D Printing: Mechanical Properties
- Resin 3D Printing vs. Filament 3D Printing: Support Structures
- Resin 3D Printing vs. Filament 3D Printing: Material Characteristics
- Resin 3D Printing vs. Filament 3D Printing: Speed and Volume Production
- Resin 3D Printing vs. Filament 3D Printing: Post-processing Requirements
- Resin 3D Printing vs. Filament 3D Printing: Environmental Impact
- Resin 3D Printing vs. Filament 3D Printing: Cost Analysis
- How to Choose Between Resin 3D Printing & Filament 3D Printing
What Is Resin 3D Printing?
Resin 3D printing, also known as Stereolithography (SLA), utilizes liquid photopolymer resin. In this process, a light source, such as a laser or projector, cures the resin selectively, hardening it layer by layer to form a solid object.
During printing, the build platform lowers into the resin vat, and the light source, guided by the 3D model’s design, solidifies specific resin areas. After each layer solidifies, the platform moves up, allowing uncured resin to cover the previous layer. This cycle repeats until the object is complete.
Advantages of Resin 3D Printing
- Excels in capturing intricate details and complex shapes, suitable for objects requiring fine features.
- Outputs parts with superior surface smoothness, minimizing post-processing efforts.
- Provides access to a variety of resins tailored for specific applications, including options that are flexible, durable, or transparent.
- Ideal for industries requiring detailed models, such as the jewelry and dental sectors, as well as for creating intricate prototypes.
- Optimal for manufacturing small quantities of items due to its detail and quality, without the need for large-scale production setups.
Disadvantages of Resin 3D Printing
- Involves handling toxic photopolymer resins, necessitating caution and proper ventilation to mitigate health risks.
- The printing and post-processing stages are typically longer, which can be less efficient for immediate or bulk needs.
- Associated expenses such as resin, specialized machinery, and maintenance are generally higher than other forms of 3D printing.
- Requires thorough post-processing, including washing off uncured resin, additional UV curing, and regular cleaning of equipment.
- Prints are often strong but can be brittle, which may limit their use in applications requiring high mechanical strength or flexibility
What Is Filament 3D Printing?
Filament 3D printing, or Fused Deposition Modeling (FDM), involves extruding a thermoplastic filament through a heated nozzle. The material melts and is deposited layer by layer to construct the 3D object.For those interested in utilizing this technology, there are various SLA 3D printing services available in 2024 that can help bring your designs to life.
This technique is popular for its simplicity and the variety of materials available, such as PLA, ABS, and PETG. The printer heats the filament, pushes it through the nozzle, and lays it down on the build platform, where it cools and solidifies to form the structure of the object. The process continues layer by layer until the entire object is fabricated.
Advantages of Filament 3D Printing
- Offers a wide range of materials with varying properties, including PLA, ABS, and PETG, suitable for different applications and requirements.
- Lower initial investment for printers and materials compared to other 3D printing technologies, making it accessible for hobbyists and small businesses.
- Straightforward setup and operation make it suitable for beginners, with extensive online communities and resources for support.
- Produces robust and functional parts suitable for a variety of applications, from prototypes to final products.
- Availability of biodegradable materials like PLA contributes to environmentally responsible printing practices.
- Capable of creating larger objects in one piece, reducing the need for assembly from multiple smaller parts.
- Often requires less finishing work than other technologies, saving time and effort after printing.
Disadvantages of Filament 3D Printing
- May not achieve the same level of detail and smooth surface finishes as resin-based printing, affecting the quality of intricate models.
- While diverse, the range of materials is not as expansive in functional properties (such as flexibility or transparency) as those available for resin printing.
- Prone to issues like warping, stringing, or layer misalignment, which can affect the final product’s aesthetic and structural integrity.
- Parts can be susceptible to heat and may deform if not designed or printed correctly, especially when using materials like ABS.
- Support structures, necessary for complex designs, can be difficult to remove and may leave marks or damage the surface.
- Although there are eco-friendly options, many common filaments are not biodegradable and contribute to plastic waste.
- Printers can be noisy during operation, and heated components present burn risks, requiring safe operating practices.
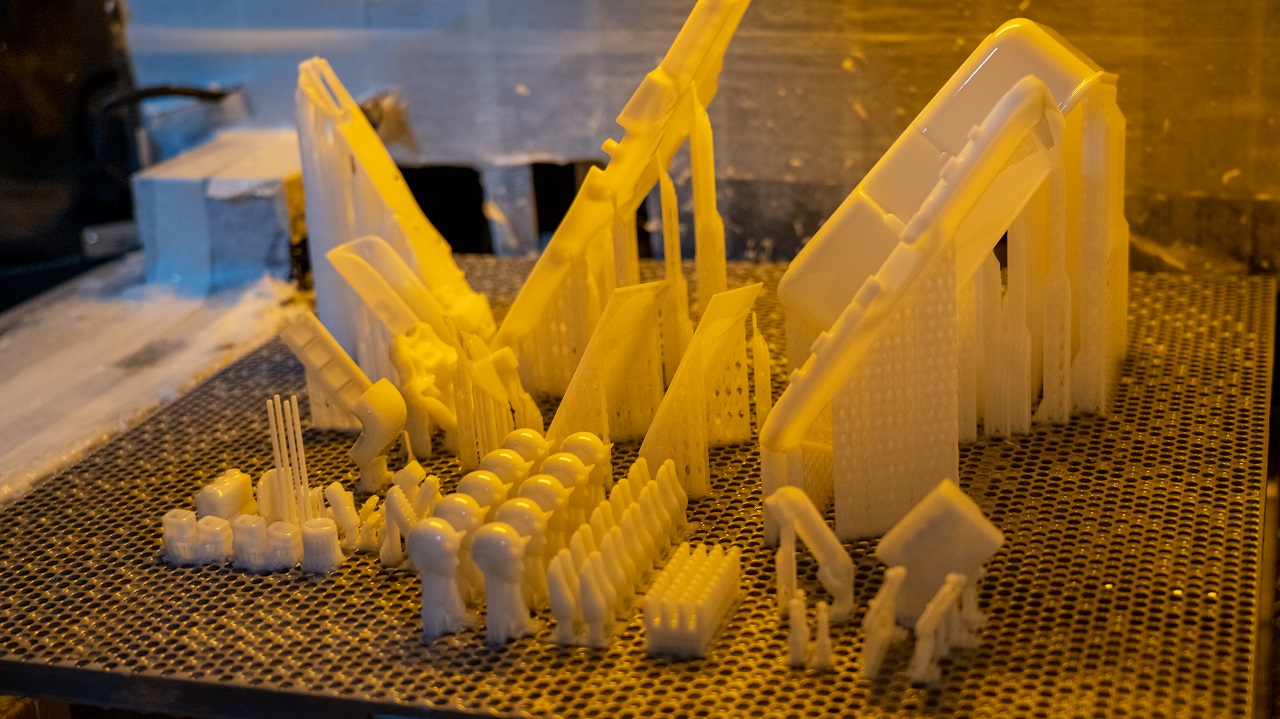

Resin 3D Printing vs. Filament 3D Printing: Accuracy and Resolutions
Resin printing, with its capability for finer details, reaches resolutions as low as 25 microns, significantly higher than the typical 100 microns for filament printing. This precision makes resin ideal for intricate designs, such as miniature models or complex jewelry. Filament printing, though less precise, has made significant strides with improved nozzle technology and tighter control systems, enhancing its resolution capabilities.
Resin 3D Printing vs. Filament 3D Printing: Mechanical Properties
Filament-based prints, particularly those made with materials like ABS or PETG, are known for their strength and durability. They can withstand physical stress and heat, making them suitable for functional parts like mechanical gears or automotive components. On the other hand, while resin prints can be rigid and detailed, they may lack the same level of impact resistance and can be more prone to brittleness, especially under prolonged UV exposure or stress.
Resin 3D Printing vs. Filament 3D Printing: Support Structures
Support structures in resin printing are integral but can lead to labor-intensive post-processing. These supports must be manually removed and the surface post-cured for proper hardness and stability, which can be time-consuming. In contrast, filament printing supports can be designed to be less dense and more easily removed, with some designs allowing for snap-off features. However, the quality of support removal in filament printing varies based on material and settings, and poor removal can impact the surface finish.
Resin 3D Printing vs. Filament 3D Printing: Material Characteristics
Resin printing materials, known as photopolymers, vary from flexible and impact-resistant to rigid and temperature-resistant, accommodating applications like medical models and transparent prototypes. However, they can be more susceptible to wear and environmental factors, such as sunlight and chemicals, leading to brittleness over time. Filament printing utilizes thermoplastics like PLA, ABS, and TPU, providing a spectrum from biodegradable options to high-strength, heat-resistant varieties. This range makes filament materials suitable for both everyday projects and functional engineering parts.
Resin 3D Printing vs. Filament 3D Printing: Speed and Volume Production
In terms of printing speed, filament printers generally operate faster, with speeds varying from 50 to 100 mm/s, making them better suited for producing larger volumes or bigger objects efficiently. Resin printers, focusing on detail, work slower, often taking hours for a single print depending on the model’s size and complexity. However, resin printers can simultaneously print multiple objects within the same build volume, which can offset the slower speed when producing numerous small items.
Resin 3D Printing vs. Filament 3D Printing: Post-processing Requirements
Resin prints require extensive post-processing, including washing in solvents like isopropyl alcohol to remove uncured resin, followed by curing under UV light to achieve full material properties. This process can be messy and time-consuming. Filament prints may need minimal post-processing, such as removing support structures and sanding for smoother finishes. The requirement for post-processing in filament printing largely depends on the print’s complexity and the material used.
| 3D Printing Technology | 3D Printing Options | Price Range |
|---|---|---|
| Resin 3D Printing | Anycubic Photon, Elegoo Mars, Formlabs Form 3 | $200 – $3,500 |
| Resin 3D Printing | Peopoly Phenom, 3D Systems ProJet | $5,000 and above |
| Filament 3D Printing | Creality Ender 3, Monoprice Select Mini | $200 – $500 |
| Filament 3D Printing | Prusa i3 series, Artillery Sidewinder X1 | $500 – $1,000 |
| Filament 3D Printing | Ultimaker S5, MakerBot Replicator+ | $5,000 and above |
There is a wide range of 3D printers available for both methods. Resin printers are generally more expensive, while filament printers can be more accessible for beginners and hobbyists.
Resin 3D Printing vs. Filament 3D Printing: Environmental Impact
Filament printing, particularly with materials like PLA (a biodegradable thermoplastic derived from renewable resources), is often viewed as more eco-friendly. However, not all filaments are biodegradable, and the energy consumption of filament printers can be high. Resin printing involves chemicals that require careful handling and disposal due to their toxic nature, posing potential environmental hazards. Moreover, uncured resin and solvent waste contribute to its environmental footprint.
Resin 3D Printing vs. Filament 3D Printing: Cost Analysis
Resin 3D printing generally incurs higher costs than filament 3D printing, with initial setup costs ranging from $200 to over $10,000 for resin printers compared to $150 to $6,000 for filament printers. Material expenses also reflect this trend, with resin costing $50 to $150 per liter, whereas filament ranges from $20 to $50 per kilogram, making filament printing more cost-effective, especially for larger projects.
Operational costs further distinguish the two, as resin printing involves higher energy consumption and additional expenses for post-processing and disposal. Despite this, resin printing may be more economical for projects requiring high detail and smooth finishes due to its superior precision. Conversely, filament printing is typically more budget-friendly for larger, less intricate items, offering lower costs per part when producing in bulk. The actual cost of 3D printing things depends on various factors, such as the technology used, material choice, and project complexity.
How to Choose Between Resin 3D Printing & Filament 3D Printing
Resin 3D printing is ideal for projects requiring high precision and detail, such as intricate jewelry, dental models, or small, complex prototypes. It is suited for those who need smooth finishes and are willing to invest in higher initial costs and handle more complex post-processing. Consider resin printing if your priorities are detail over size and you are prepared for the associated costs and safety measures.
In contrast, filament 3D printing is better suited for larger projects, functional parts, or items that require less detail but greater structural integrity. It’s a more cost-effective solution for beginners and hobbyists due to lower initial and material costs. If you prefer a simpler, user-friendly process, need to produce larger items, or are looking for a more affordable option, check out QSY’s online 3D printing services!